Creativity leads to innovation that improves organizational functioning by solving problems. As more problems are resolved, the organization continues growing to become competitive on the market. Even though the subconscious influences creativity and problem solving, it is has been ignored as pseudo-science despite impacting almost everything in our lives; including solving business problems.
Creativity relies on our ability to resolve problems that lead to the survival of both ourselves and society. Creative people like Einstein are honored because they have the capacity to develop new solutions to long unsolved problems. Without the use of the subconscious, creativity would have never been turned into a useful form.
Problem-solving requires preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification (Grupas, 1990). A creative person studies a problem and develops a knowledge base, allows possible solutions to incubate in the subconscious, percolates a solution into a conscious form that is verified through research.
The reason the subconscious is so powerful is that it is a self-organizing system that continually makes associations/connections between information (Andreasen, 2011). As the brain builds framework for handling environmental knowledge, it also connects, categories and comes to conclusions of perplexing problems.
The speed and ability of the mind to do this is based on the intelligence level of the individual. Intelligent people are better able to process greater amounts of information and find associations faster. When put to substantial use that innovative creativity has tangible value for business that want to invent new ways of doing things.
People with creative minds don’t often think like everyone else. They use a divergent system of reasoning that creates many different solutions that are eventually pruned back to the most useful ones. This is in contrast to the general population that has been socialized through schooling to use convergent thinking that relies on step-by-step processing models already planned out by someone else.
Divergent thinking can cause difficulties interacting with people. Many intelligent people lose jobs and opportunities only because of the restrictive social circles inherent in most businesses. They may say things that are true but also run against conventional wisdom that doesn’t sit well with ego driven individuals.
Open environments that respect the diversities of people, and the way in which people process information, are more likely to develop innovative environments. Restrictive, position-oriented, highly controlled conditions will restrict innovation. By developing the right open-minded environment, a company can foster the bringing forward of subconscious ideas to develop higher forms of intellectual capital.
The blog discusses current affairs and development of national economic and social health through unique idea generation. Consider the blog a type of thought experiment where ideas are generated to be pondered but should never be considered definitive as a final conclusion. It is just a pathway to understanding and one may equally reject as accept ideas as theoretical dribble. New perspectives, new opportunities, for a new generation. “The price of freedom is eternal vigilance.”—Thomas Jefferson
Showing posts with label intellectual capital. Show all posts
Showing posts with label intellectual capital. Show all posts
Sunday, June 7, 2015
Wednesday, January 14, 2015
The Importance of Hiring Managers with Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking allows managers
to find new solutions to existing organizational problems. Those that can see a
problem from multiple perspectives are more likely to come to comprehensive solutions with greater impact. Tunnel Vision among managers leads to lower
results and less innovative problem solving. Companies that do not consider adding divergent thinking skills to their intellectual and labor capital may find themselves with sluggish future performance.
Divergent thinking is a process of developing multiple
vantage points and ways of seeing a problem. Those with higher cognitive
abilities often use multiple and simultaneous pathways to understand, analyse, solve, and implement solutions from different vantage points. Switching perspectives is important for well-rounded solutions that meet multiple stakeholder solutions.
Divergent thinking is associated with genius and artistic ability.
Neuroscientific studies have found that divergent thinking uses both
hemispheres and causes higher levels of neural activation (Yoruk & Runco,
2014). Divergent thinking activates the central, temporal, and parietal regions
of the brain to develop semantic processing. Semantic processing is a deeper processing than most people are capable and allows for the encoding of meaning.
A high percentage of managers have tunnel vision and know all the answers without exploring any of the premises. Their level of mental processing is low and relies on snap judgments, hueristics and bias. This tunnel vision becomes obvious when a person cannot find multiple explanations of a problem or accept the possibilities of other alternative solutions. It is often manifested in “know it all”, close-minded, and rigid explanations.
Most of us have probably met at one time a manager who knew all the answers, used their power to force their opinion, and ultimately was gravely mistaken in their conclusions. When executives are stuck in tunnel vision they can cost companies a lot of money as their erroneous assumptions make their way throughout their department. Strong executives explore all the possibilities to find that which is most likely to work.
A high percentage of managers have tunnel vision and know all the answers without exploring any of the premises. Their level of mental processing is low and relies on snap judgments, hueristics and bias. This tunnel vision becomes obvious when a person cannot find multiple explanations of a problem or accept the possibilities of other alternative solutions. It is often manifested in “know it all”, close-minded, and rigid explanations.
Most of us have probably met at one time a manager who knew all the answers, used their power to force their opinion, and ultimately was gravely mistaken in their conclusions. When executives are stuck in tunnel vision they can cost companies a lot of money as their erroneous assumptions make their way throughout their department. Strong executives explore all the possibilities to find that which is most likely to work.
Tunnel vision is dangerous for organizations because
managers who cannot see alternative possibilities run the same poor processes until they collapse. They are also likely to use the same mental tool to solve every problem. Each major problem needs its own tool from the tool shed. Tunnel vision won't even allow them to see where the tool shed is let alone what other tools it contains.
Based upon an in-depth study of 221 managers within the workplace it was found that divergent thinking and openness come together (Scratchley &
Hakstian, 2001). Managers who are open to new experiences and abilities are
better at finding new ways of thinking about things. Hence, narrow
minded individuals who are convinced of their “rightness” should be avoided at
all costs.
A few tips for improving divergent thinking in your company may be beneficial.
A few tips for improving divergent thinking in your company may be beneficial.
Switch Up the Executive Team: If your organization is suffering from stuffy thoughts and rehashed ideas then consider switching up your executive team. Hire
some new talent, throw out a few of the old talent, and get a different way of evaluating problems.
Rearrange Team
Membership: In some organizations the same people are asked to join problem solving teams. Ensuring you are using different types of
people with various backgrounds and collaborative departments will help create new ways of
thinking about issues.
Hire Creative and Open
Minded People: Without having people with the cognitive ability to solve problems and create organizational innovation, the company will eventually move into the decline stage. Develop stronger selection tools that look for creativeness and open mindedness.
Adjust Performance Metrics: What and how we reward people impacts what type of behavior they are going to exhibit. If you want them to be creative and solve problems then ensure it is reflective as a performance evaluation.
Develop an Inclusive Culture: Creative people don't come forward with ideas in hostile environments. To propose solutions requires a level of risk and a receptive environment that doesn't chastise new ideas.
Train Managers to be Critical Thinkers: Even though much is determined by personality it is still possible to train managers on to use critical thinking and make decisions is beneficial; whether or not they use them is another story.
Scratchley, L. & Hakstiane, R. (2001). The measurement
and prediction of managerial creativity. Creativity
Research Journal, 13 (3/4).
Yoruk, S. &
Runco, M. (2014). The neuroscience of divergent thinking. Actitas Nervosa Superior, 56 (1/2).
Saturday, November 16, 2013
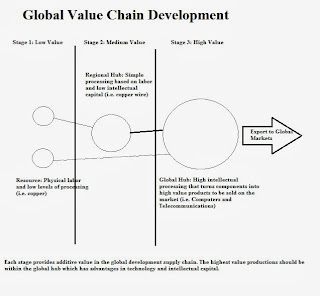
Free Trade Agreements can Foster Economic Hubs
Free trade agreements are a common economic method
of increasing trade. Free trade agreements work best where lower value imports
are used to create higher value exports. Global hubs often work with regional hubs in an international
supply chain that continues to develop products for exportation to world
markets. Effective economic hubs use intellectual capital to create value that
cannot be easily copied by other countries.
According to Chong and Hur (2008) each hub has
access through trade agreements to the spokes but the spokes only have access
to the hub. This means that the hub can sell more products and services than
the spokes can themselves. This advantage gives them preferred trading and
profitability standards. It also creates a value chain with the highest hub
realizing the most benefits.
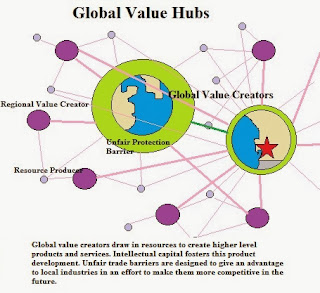 Because hubs are central locations, they also can have
an advantage in investments (Wonnacott, 1996). Those who seek to maximize their
investment opportunities will invest their money through the purchasing of
stocks or starting businesses within the hub (i.e. supply chain). They are
aware that this is the fastest place for them to grow their capital. This in
turn spurs additional economic growth in the area and develops opportunities
for product development.
Because hubs are central locations, they also can have
an advantage in investments (Wonnacott, 1996). Those who seek to maximize their
investment opportunities will invest their money through the purchasing of
stocks or starting businesses within the hub (i.e. supply chain). They are
aware that this is the fastest place for them to grow their capital. This in
turn spurs additional economic growth in the area and develops opportunities
for product development.
A problem occurs when two mega hubs are not
competing on the same assumptions. For example, Chinese tariffs on U.S. made
automotive products are designed to protect Chinese budding suppliers (Jian,
2008). When this occurs, one country has an advantage as they are willing to
sell their products without tariffs to the U.S. but will not accept American
products. The free trade cycle is broken.
In order for the mega hubs to operate correctly
individual components of production should be purchased at a lower price and
then assembled with intellectual labor into higher value products that are sold
on the market. If these products are built else ware and sold primarily within
the U.S. there is no export advantage, revenue, or growth. A decline occurs
because the consumer culture is soaking up the value locally instead of
properly exporting.
Hubs should
be creators of wealth. They should use both imported and locally generated
resources to develop them into higher value products for export. When this does
not occur, it is likely that the export gain will turn into an import loss.
Those hubs that export products will grow while those that only distribute
imported products are likely to decline. It is the total value of the flow that
determines growth or decline in regional development.
Chong, S. & Hur, J. (2008).
Small hubs, large spokes and overlapping free trade agreements. World Economy, 31 (2).
Jain, Y. (2008). Wto rips china’s
tariffs on imported auto parts. Automotive News, 82 (6295).
Wonnacott, R. J. (1996a), ‘Free-Trade
Agreements: For Better or Worse?’, American Economic
Review,
86,
2, 62–66.
Saturday, February 16, 2013
Retaining Competitive Advantages through Specialized Human Capital
Organizations seek to develop uniqueness that will
allow them to create competitive advantages that allow them to better compete
on international markets. The combination of human capital and organizational
factors helps develop those firm specific qualities. The development of human
capital through firm-specific skills will further retain the talent of
organizational members and encourage lower levels of knowledge loss or
competitive posturing.
Competitive advantage is a unique organizational strength
a company develops over competitors through the offering of higher products,
value, or benefits that justifies higher prices on the market. It is a
condition whereby an organization is more efficient and productive than those it
competes with. Such firms are seen as competitive, “if it is able to create more economic value than the marginal
competitor (Peteraf & Barney, 2003: 314). Through this competitiveness,
additional benefits are earned by the organization that other companies have a
hard time emulating.
Competitive advantage can be found in the
development of human capital within an organization. Such competitive advantage
comes from employee skills and abilities that cannot be easily passed from one
firm to another (Kor & Leblebici, 2005). Thus skills and abilities help
employees work in patterns and methods that other organizations will have
difficulty time copying without copying all of the unique aspects of the firm.
Skills and abilities can be developed within other
organizations which reduces the overall competitiveness of the subject firm.
However, even though such skills apply to other firms their true value lies in
their combination of technology, product markets and assets (Teece, 1986). Such
firms are able to combine the various components that create uniqueness in
order to develop new market strengths. It is this combination of strengths that
is difficult for organizations to develop without significant research, cost
and energy.
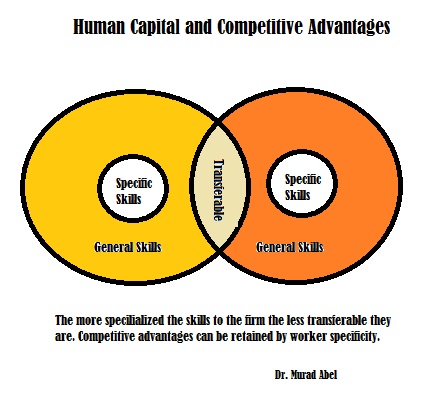
To develop competitive advantage through human
capital it is important to see employee skills as a total portfolio that
fosters firm strength. Some skills are general while others are more firm
specific (Lazear, 2009). It is the firm specific skills that have the highest
value and exchange rate with the organization. It is through the development of
employee skill specificity that organizations can not only create competitive
advantages in human capital but also the ability to retain such capital due to
its value being tied to the firm.
Let us take an example. Two employees are seeking
higher paychecks. Each has their own particular portfolio of skills and
abilities. The organization that understands the unique skills and abilities of
their employees can combine other assets to drive higher levels of unique
competitive advantages. In this example, employee 1 has skills that are unique
to the firm while employee 2 has skills that are more general. Employee 1 is
likely to be retained by the firm because their skills are non-transferrable.
Employee 2 can apply their skills wherever they decide to work and are more
likely to move to another company.
Firm specific capital is difficult to transfer to
other companies (Hashimoto, 1981). The more specialized the employee and their
abilities the less opportunity they have to move to a competitor and obtain comparative
wages and income. This specialization makes their value worth more to the home
firm where they are likely to be paid the highest rate of income.
Developing competitive advantages means combining
the organizations unique qualities with available human capital to develop
strengths that other firms cannot copy. Organizations that develop specific
firm related skills are less likely to lose this intellectual capital to other
companies that do not have the same needs. General skills provide appropriate
foundations for human capital development but can be easily transferred from
one firm to the next. Employees will also desire to retain employment as their
firm specific skills have the highest exchange rates of value. To develop
stronger competitive advantages requires the ability to take general skills and
foster firm specific skills that have the highest competitive advantage for
both the employee and the company by retaining employment.
Hashimoto, M. (1981). Firm-specific human capital as
a shared investment. American Economic
Review, 71: 475–482.
Kor, Y. & Leblebici, H. (2005). How do
interdependencies among human-capital deployment, development, and diversification
strategies affect firms’ financial performance? Strategic Management Journal, 26: 967–985.
Lazear, E. (2009). Firm-specific human capital: A
skill weights approach. Journal of
Political Economy, 117: 914-990.
Peteraf, M. & Barney, J. (2003). Unraveling the
resource based tangle. Managerial and
Decision Economics, 24: 309–323.
Teece, D. (1986). Profiting from technological
innovation: Implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public
policy. Research Policy, 15: 285–305.
Bookmark with Your Social Network
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)